Types of Liver Diseases and Disorders in Human Beings
There are various types of liver diseases. In this article, you will find a list of liver diseases of various different kinds. But, it is not the exhaustive list. Enlisting all the hepatic disorders is beyond the perimeter of this article.
A brief discussion of only a few of these disorders will appear at the end of this list. Meanwhile, you will also learn about the liver disease symptoms, tests, causes and remedies.
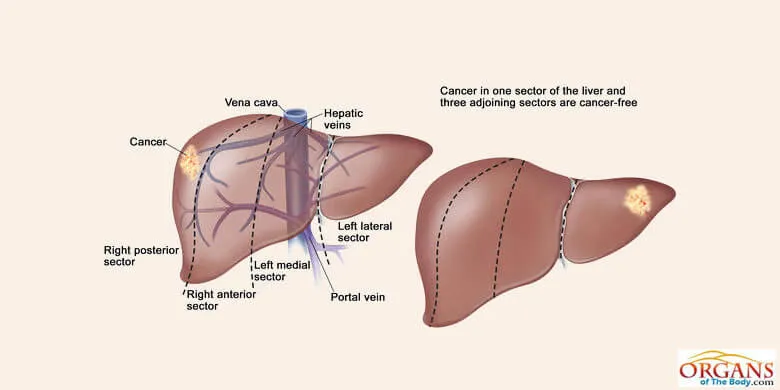
Types of Liver Diseases
- Jaundice – High levels of bilirubin cause yellowing of the skin and the white of the eyes.
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E – These are different types of liver diseases that occur by the attack of different types of viruses.
- Drug-induced hepatotoxicity, as the name suggests, is the result of harmful effects of drugs on the liver. The drug induced hepatotoxicity is one of the common liver diseases.
- Alcoholic liver disease – It results from the excessive use of alcoholic drinks.
- Fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) – FHF is condition of acute live failure which severely impairs synthetic function of the organ.
- Drug-induced chronic hepatitis – Excessive use of drugs causes inflammation of liver which may last for six months or more.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – When there is the storage of too much fat in the liver, it leads to non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in the people who consume little to no alcohol.
- Cirrhosis – Usually, developing over months or years, it affects the functioning of liver. There are only a few or no specific signs.
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome (BCS) – BCS is a rare liver condition which results from the obstruction in the hepatic veins.
- Fibropolycystic liver diseases – In this group of congenital disorders, there is the formation of lesions in the liver in the bile ducts. Here the causative agent is the abnormal embryologic development of the ductal plates.
- Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome – The exposure to toxins and drugs is the major contributing factor towards the development of this fatal form of hepatic injury.
- Liver abscess – The abdominal infections, like appendicitis and diverticulitis, trigger the formation of pus-filled mass inside the organ.
- Liver tumors – The benign or noncancerous liver tumors, usually, do not pose a serious risk for health. The malignant or cancerous liver tumors, on the other hand, pose a serious health risk. They can be either primary or metastatic. The first type, i.e. the primary hepatic tumors originate in the liver. In the second type, i.e. the metastatic liver tumor, the cancer develops elsewhere in the body and spreads to the liver.
- Wilson's disease – The Wilson’s disease is a rare type of the recessive autosomal congenital disease. In this case, there is an abnormal copper metabolism in the body. Consequently, there is the accumulation of copper especially in the liver and the brain. If you do not treat it timely, the condition can also claim the life of the victim.
- Hemochromatosis – In this genetic disorder, there is excessive accumulation of iron in the organs, like liver. On the other hand, too much amount of iron leads to liver toxicity.
It was a list of liver diseases of several kinds. The common types of liver disease, from this list, are being briefly discussed in the following part of the article.
Jaundice
Jaundice is one of the common types of liver diseases that refers to the golden yellow appearance of skin and sclera. It results from too much accumulation of bilirubin in the body fluids. Jaundice is first noticeable in the sclera of the eyes. You call this yellow discoloration of the sclera as icterus. Jaundice is evident in skin when serum bilirubin level is 2.5 to 3 mg/dL.
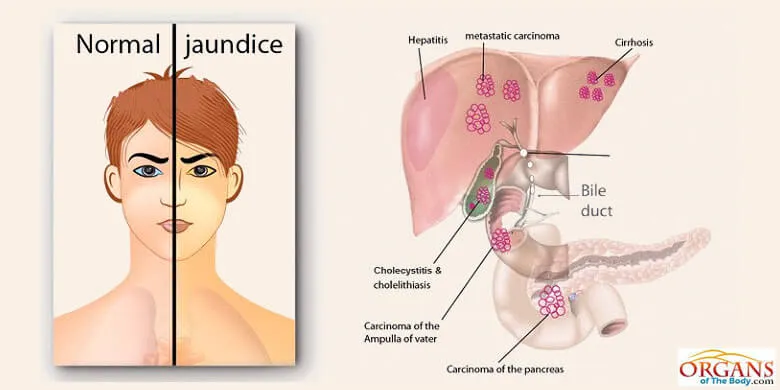
Causes of Jaundice:
- Overproduction of bilirubin.
- Less hepatic uptake of bilirubin
- Impaired conjugation of bilirubin
- Defective hepatocellular excretion of bilirubin
Symptoms of Jaundice:
- The most significant symptom is the yellowing of the skin and the sclera, i.e. the white part of your eyes.
- Abdominal pain which is characteristic of the blockage in the bile duct.
- Other symptoms include fever, fatigue, vomiting and the weight loss, etc.
Treatment of Jaundice:
The hike in bilirubin level is actually due to the rapid breakdown of red blood cells. This occurs due to some disease and infection that also affects liver. So, the treatment of jaundice completely depends on the cure of underlying cause. In other words, you have to identify and treat the condition that is responsible for the higher level of bilirubin in the body.
Drug-induced Hepatotoxicity
As the very name implies, drug-induced hepatotoxicity is one of the types of liver diseases which occur due to the effect of drugs on liver. Many drugs can harm the liver severely. Therefore, it is always wiser to consult a health professional before taking any medicine. And you should refrain from self-medication.
Causes of Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity:
Here are some of the harmful drugs which lead to different types of liver diseases:
- Acetaminophen – The drug can cause necrosis or injury and death of the hepatocytes, i.e. the liver cells.
- Oral contraceptives – Hepatic adenoma may result from the harmful effects of oral contraceptives.
- Halothane – The use of halothane puts the individuals at the risk of developing fulminant hepatitis.
- Sulfonamides – With the intake of sulfonamides, you may fall victim to granulomatous. As a result, the phagocytes are unable to kill some types of fungi and the bacterial species.
- Phenytoin, isoniazid – These drugs can lead to the development of acute and chronic hepatitis.
- Methotrexate, amiodarone – Different types of liver diseases, like fibrosis and cirrhosis may result from the use of methotrexate and amiodarone, etc.
- Chlorpromazine – If you take chlorpromazine, you would be at the risk of cholestasis.
Alcoholic liver disease
The overuse of alcohol can cause several types of liver diseases. They include the buildup of fat in the liver, alcoholic cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, and so on. In comparison with men, women seem to be more susceptible to alcoholic liver injury.
Alcoholic cirrhosis which develops in 15% of the alcoholics is the most common disease that requires liver transplantation in adults.
Symptoms of Alcoholic Liver Disease:
As a result of the alcoholic liver disease, the patient may develop following symptoms:
- Loss of appetite followed by the weight loss.
- Fatigue due to the lack of energy, and it can be debilitating.
- Appearance of the characteristic symptoms of the jaundice, for example, yellowing of the skin and sclera.
- Retention of fluid and inflammation in legs, ankles and the abdominal region, etc.
Treatment of Alcoholic Live Disease:
The first step towards the treatment of this condition is to abstain from alcohol. However, the suggestion of a particular treatment strategy depends on the specific type of alcohol-related liver disorder.
Nevertheless, in all such conditions, the cessation of alcohol is essential. In this way, you can prevent the liver from further damage. On the other hand, the use of medication will help liver synthesize its damaged cells.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is an end-stage liver disease. Here alcohol is the direct hepatotoxin. And it is the most common cause of cirrhosis in the western world. In cirrhosis, there is total disruption of the liver architecture due to fibrosis and nodule formation.
This disruption in the liver architecture eventually interferes with liver blood flow and function.
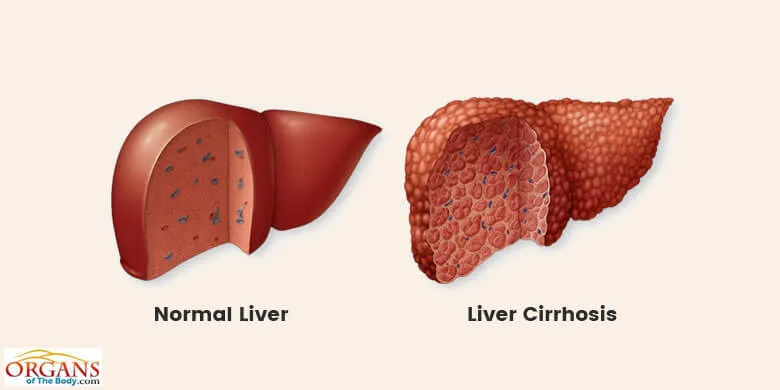
Cirrhosis Causes:
- Too much consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Blockage in the bile duct which may be due to some other liver disease.
- Buildup of fats in the organ.
- Chronic viral infections, for example, hepatitis B and C.
Cirrhosis Treatment:
Usually, no medication can reverse the damage that has occurred to the liver due to cirrhosis. However, certain medicines can stop further damage to the organ. In this regard, the changes in lifestyle will also be helpful. Nevertheless, the best treatment option is to go for the liver transplant. It will restore the normal function of the organ.
Liver Function Tests
Initially, the healthcare providers employ a number of liver function tests for the evaluation of different types of liver diseases. A single abnormal laboratory test value may not confirm a specific liver disease. That is why it is wiser to look for consistently abnormal lab values in more than one liver function tests.
It is also essential to repeat certain tests on more than one occasion. In this way, you will get a diagnostic pattern. Followings are the liver function tests for different types of liver diseases.
- Serum bilirubin – How much bilirubin is present in the serum?
- Urine bilirubin – That is, find out the amount of bilirubin in urine.
- Blood ammonia – Determine the quantity of ammonia in the blood of patient.
- AST or Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) – It involves measuring the quantity of AST enzyme in the blood serum.
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) – The purpose of this test is to find out the amount of ALT enzyme in the blood.
- ALP or alkaline phosphatase – The alkaline phosphatase enzyme helps in the breakdown of proteins. An ALP test will help to determine the lever damage.
- Albumin in Serum – The test for albumin protein in the blood will serve as an indicator for the liver diseases.
- Globulins in Blood – The globulins test aims at measuring the quantity of globulin proteins in the serum.
- Serum Prothrombin Time – The prothrombin test involves the measurement of time your blood takes to clot.
Other diagnostic tests may include ultrasonography and liver biopsy. Liver biopsy remains the most accurate means of assessing the severity and stage of several types of liver diseases. It is also a useful technique for diagnosis. Through this, you can also predict prognosis and monitor response to the treatment.
Causes of Acute and Chronic Types of Liver Diseases
The most common causes of acute liver disease (less than 6 months) are:
- Viral Hepatitis – Viral infection of liver occurs due to the attack of hepatitis B or C virus, etc.
- Drug-induced Liver Injury – In this type of injury, drugs cause a damage to the liver.
- Cholangitis (Inflammation of Bile Duct) – There is blockage in the bile duct which leads to its swelling.
- Alcohol Abuse – Consuming too much alcohol is injurious to the health of liver. The alcohol addict is likely to fall victim to a number of different types of liver diseases.
The most common causes of chronic liver disease (Greater than 6 months) are:
- Chronic Hepatitis C – The chronic hepatitis C serves as one of the major causes for the chronic liver disease.
- Alcohol Abuse – Alcoholism can be the cause of both acute and chronic hepatic disorders.
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis – When hepatitis does not occur due to alcohol abuse, it is called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Chronic Hepatitis B – This viral infection results in the scaring, failure and cancer of the liver.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis – In the autoimmune hepatitis, the immune system attacks and damages the liver cells and components.
- Sclerosing Cholangitis – The chronic liver condition of sclerosing cholangitis involves the swelling and fibrosis of the bile ducts.
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis – This autoimmune disorder causes slow destruction of the small bile ducts.
- Hemochromatosis – As the name indicates, it involves excessive accumulation of iron in the organ.
- Wilson's Disease – The Wilson’s disease is the result of excessive copper accumulation in the organ.
Liver transplantation
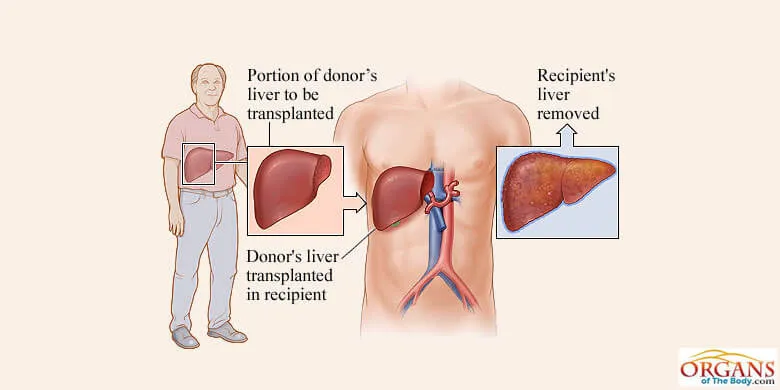 It is the surgical means to replace a diseased liver with a normal organ. The transplant is the only choice for patients with end-stage liver. Actually, their chronic or acute liver disease is progressive, life threatening and unresponsive to medical therapy.
It is the surgical means to replace a diseased liver with a normal organ. The transplant is the only choice for patients with end-stage liver. Actually, their chronic or acute liver disease is progressive, life threatening and unresponsive to medical therapy.
After the transplantation, for low risk patients, current level of success or survival rate is approximately 90% for one year and 60% for five years. But, for high risk patients, i.e. those suffering from cancer, fulminant hepatitis, and having age more than 65, the success rate is different. The current survival rate for them is approximately 60% for one year and 35% for five years.


