What is Adrenal Gland?
Did you ever experience an adrenaline rush? For this purpose, you need to know what is adrenal gland? Just go through its definition and functions. Also you should see them in the pictures. They appear as small structure and are attached to the top of kidneys. These organs produce different types of hormones of vital importance. The adrenal gland disorders seriously affect their performance. Just read on to learn details about what is adrenal gland.
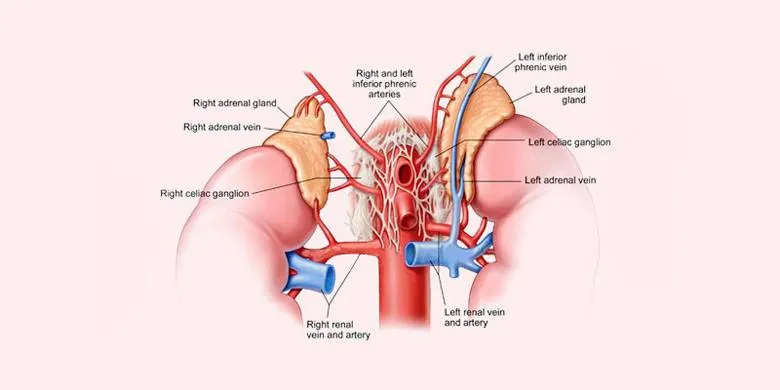
Adrenal Gland Definition:
The glands responsible for the production of adrenaline are known as adrenal glands, also called emergency glands. The hormones help you cope with situations of extreme stress, danger or excitement. They not only produce adrenaline, but several other hormones as well. These hormones are important for different functions of our body.
Adrenaline and noradrenalin are notable hormones of adrenal glands. Another main class of hormones is that of corticosteroid hormones. To know completely What is Adrenal Gland, you also need to know about the structure and location of these organs of the body as well.
Adrenal glands function is to produce corticosteroids. The pituitary gland stimulates them for work. In turn, the pituitary is stimulated by the hypothalamus. In other words, the secretion of hormones is controlled by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus.
Anatomy of Adrenal Glands: Layer-by-Layer Analysis of The Structure of These Glands
The Adrenal Gland consists of three layers of the adrenal cortex. The first layer is known as Zona Glomerulosa, the second layer is named as Zona Fasciculata, the third layer is called Zone Reticularis, and the innermost layer is called Adrenal Medulla. The structure and function of each of these layers is different from each other. Lets discuss this one by one.
The Unique Nature of Adrenal Glands: A Layer by Layer Study
The blood enters into the first layer and then travel to the next layer until it reaches the last part of the glands.
1. Layer-1 is Zone Glomerulosa and read its function
In Zona Glomerulosa, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) acts on cholesterol and converts it into pregnenolone and then into progesterone.
a. What Zone Glomerulosa Performs?
The first layer of the adrenal cortex helps in maintaining blood volume, ECF, homeostasis, and life and prevents death.
b. Results of Malfunctioning of Zone Glomerulosa
The deficiency of this layer leads to hyponatremia (low sodium content), low blood pressure, and death within a few days. Increased production of aldosterone leads to hypertension and many associated health problems.
2. Layer-2 is Zona Fasciculata and read its function
Pregnenolone and progesterone travel in the blood from Zona Glomerulosa to the next layer named as Zona Fasciculata. Then pregnenolone is converted into 17-áOH pregnenolone and progesterone into 17-áOH progesterone. 21-hydroxylase acts on 17-áOH progesterone and converts it into 11-deoxycortisone and glucocorticoid (cortisol).
a. Results of Malfunctioning of Zona Fasciculata
Cortisol increases blood glucose levels and helps in maintaining homeostasis. Increased production of cortisol leads to Diabetes Mellitus, hypertension, and other associated constitutional health issues.
3. Layer-3 is Zona Reticularis; read its function
17-áOH pregnenolone and 17-áOH progesterone from Zona Fasciculata travels to the third layer, Zona Reticularis. In this layer, 17-áOH pregnenolone is converted into dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). 17-áOH progesterone, in turn, is converted into androstenedione. It is converted into testosterone and estrogen, Ojas/Tejas energy.
a. Results of Malfunctioning of Zona Fasciculata
These hormones play an important role in the maintenance of normal body temperature.
4. Layer-3 is Adrenal Medulla; read its functions
The blood with cortisol hormone then travels to the innermost layer, the adrenal medulla, which in turn produces catecholamines with the help of amino acid tyrosine.
Question: How blood receives hormones from the layers of adrenal glands one by one?
The blood enters the first layer through the capsule of the gland and then via the portal system goes to the second, third, and inner layers of the adrenal gland. While travelling from one layer to another, different elements in the blood converts into other elements.
Adrenal Gland Fatigue:
Do you know what is adrenal gland fatigue? The term seems intriguing. In fact, it is a syndrome or a collection of symptoms and signs. The condition results from the abnormal functioning of the suprarenal glands. You can cure it also with the help of an effective diet plan. The diet is inexpensive and easily available. It consists of fruits, vegetables, nuts and certain other things.
Other Topics Of Adrenal Glands
- What are the functions of the cortisol hormone?
- Which hormone controls blood pressure and depression?
- Which glands enable the animal to face physical and emotional stress?


