Top 10 Human Mouth Parts, Definition, Function, Structure
What is Mouth?
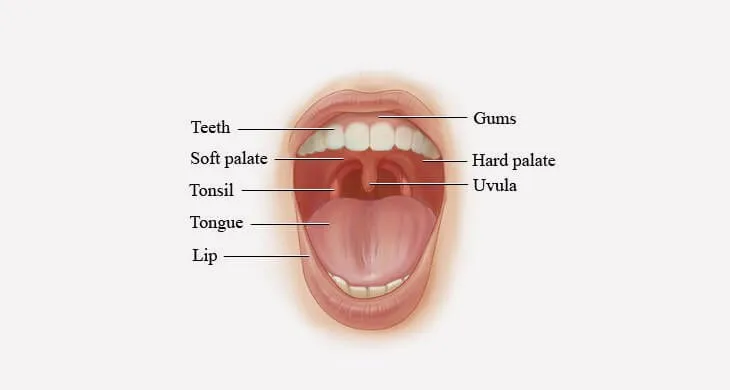
A precise answer to what is mouth is that it is the anterior most part of the gastrointestinal tract. According to mouth definition, this organ is also known as the oral cavity. This cavity contains several different other organs. Organs in the oral cavity include uvula, palate, teeth, tongue, and so on.
In the pictures about what is mouth, you can distinguish the palate into soft palate and hard palate. Each type has got its own role to play in the mouth. On the other hand, different structures of the human mouth perform a number of important functions. They include sound production, breathing, tasting, and grinding and masticating food, etc. Below is further detail about what is mouth.
Secretion of saliva is also a mouth function. Meanwhile, there are several articulatory and static organs in the oral chamber. They significantly contribute to the production and modification of sounds. Initially, the sounds start from the vibration of vocal cords in the laryngeal cavity.
Another name for the laryngeal cavity is the voice box. A number of mild and critical mouth diseases have been affecting one of the most important organs of your body.There are almost 80 organs in a human body which vary according to their sizes, functions or actions. An organ is a collection of millions of cells which group together to perform single functions in a our body. Some of these conditions do not even require formal treatment.
In other words, you can easily cure them by proper modifications in the behavior. However, other diseases need urgent, prolonged and very expensive treatment measures. Such measures include medications and surgical therapy.
Mouth Parts
Study of mouth parts is pertinent to the topic what is mouth. Moving in sequence from anterior to the posterior, you will come across different mouth parts. These are: lips, teeth, tongue, alveolar ridge, soft and hard palate, uvula and throat. The small, fleshy and muscular organ attached to the floor of your mouth that helps in tasting, chewing, swallowing and speaking is called tongue. The teeth ridge or gum ridge are alternative names for the alveolar ridge.
However, if you look at the human mouth externally, many structures of the front part of head may be included in it. They collectively form the facial organs, namely, lips, nose, chin, cheeks, eyes, eyebrows and forehead.
Lips are the soft, movable and flexible muscular structures. They are under the voluntary control of an individual. Therefore, you can open, close, or round them at will. In digestive system, their function is to serves as a passage for dietary and fluid intake.
While studying what is mouth, you should note that the mouth parts also have a role in the exchange of respiratory gases. In the production of speech, the tactile sensory organs contribute to the articulation and modification of sounds, such as bilabials, plosives, labiodentals, etc.
Mouth Function
Mouth has various internal and external structures. They all contribute to the execution of many systems in the body. For example, respiratory, digestive, sensory, secretary and phonetic systems, etc. all use mouth as a complementary organ. It means the knowledge of what is mouth is very important in the study of all these systems. Below is a brief description of some of the important mouth functions.
Mouth as a Respiratory Organs:
As a respiratory organ, the oral chamber forms first part of the air canal or respiratory canal. Primarily, it serves as a passage of airstream. Its second job is to protect the trachea and lungs against the harmful environmental substances.
Mouth as a Digestive Organ:
As a digestive organ, you can identify several important functions of mouth. For example, mouth is an organ for tasting, grinding, moistening, and partial digestion of food. Excretion of saliva, and pushing the bolus into the esophagus are some of its other jobs.
On the other hand, the function of the esophagus is to transport the food from mouth to the stomach. Here, peristaltic movements assist in the smooth and unidirectional traffic of food bolus.
Mouth as a Sensory Organ:
There are many interesting things about what is mouth. It one of the human mouth facts that tongue performs the sensory and erogenous functions, such as taste. On the other hand, lips help in the selection of food. They also have a role in love making activities and sexual arousal.
Mouth as a Secretary Organ:
Carrying out secretions is one of the jobs of your mouth. For this purpose, there are a number of glandular structures. You can find such structures at various points in and around the oral chamber. They include sublingual, submandibular and parotid glands. Meanwhile, there are as many as 800 other smaller glands.
Mouth as a Speech Organ:
The oral cavity contributes a lot to phonation and modification of linguistic sounds. The humans utilize this significant function of mouth for communication purposes. At the same time, you also know that it is the ability to speak that distinguishes humans from animals.
Mouth Diseases
The mouth is one of the principal organs in your body. Also it is a complementary structure of many systems. Therefore, the ailments of mouth not only disturb the vital mechanisms but also give rise to several other diseases. Some disorders may also claim the life of the victim.
Some of the frequently occurring oral diseases are stomatitis, oral lichen planus, mouth ulcer and traumatic ulceration, etc. There are a number of mouth diseases which affect individuals of all ages. Some occur due to microbial infections while others develop because of certain nutritional deficiencies. Although the symptoms vary. Below is the brief description of some oral conditions.
Stomatitis:
There are certain local factors that cause and intensify the oral condition, stomatitis. It is characterized by the inflammatory infections of oral mucosa.
Stomatitis Symptoms:
- Inflammation of mouth and the development of sores.
- Difficulty in eating, talking and sleeping.
- Sores can be of two types, namely, canker sores and cold sores.
- Pain in the sores.
Stomatitis Treatment:
Generally, the sores disappear within two weeks without any treatment. On the other hand, if the painful symptoms persist, the doctors have to suggest an appropriate treatment method. The choice of treatment depends on the cause behind the development of sores. If the reasons are unknown, your healthcare provider will try to alleviate the symptoms.
Oral Lichen Planus:
It is one of the types of erosive lichen planus. The oral lichen planus manifests itself through certain obvious diagnostic symptoms. For example, white patches may appear at any site in the oral cavity.
Oral Lichen Planus Symptoms:
- Dryness of mouth with a metallic, burning taste.
- Appearance of white patches on your gums, cheeks and tongue.
- Painful and burning sensation in the sores which aggravates as you eat salty or spicy foods.
- Patients face problems while taking caffeinated drinks.
Oral Lichen Planus Treatment:
A slight roughness in your mouth does not need any treatment. On the other hand, if you have developed sores and are suffering from severe pain, you will need proper treatment. In such a case, the doctors may prescribe steroid pills. Meanwhile, the corticosteroid creams are also very helpful.
Mouth Ulcer:
Mouth ulcer constitutes one of the most frequently occurring oral abnormalities. Such conditions may affect almost every individual in the world. Some of the obvious causes include the intake of hot foods or drinks and jagged teeth. Meanwhile, the use of strong mouthwashes and antiseptics can damage the lining of oral cavity.
Mouth Ulcer Symptoms:
- Appearance of round sores inside your mouth.
- Inflammation of skin around the sores.
- Sour, salty and spicy foods may cause irritation in the sores.
- Tenderness causes problems with chewing and tooth brushing.
- Loss of appetite.
Mouth Ulcer Treatment:
Interestingly, the sores in mouth ulcer disappear on their own in one to two weeks without requiring any treatment. In case, the sores are large and persistent, your healthcare provider may prescribe certain medications. For example, a corticosteroid ointment and an anti-microbial mouth rinse can alleviate symptoms of pain and irritation.


