Symptoms of GallBladder Disease in Humans - Males and Females
Human Gallbladder — An Overview:
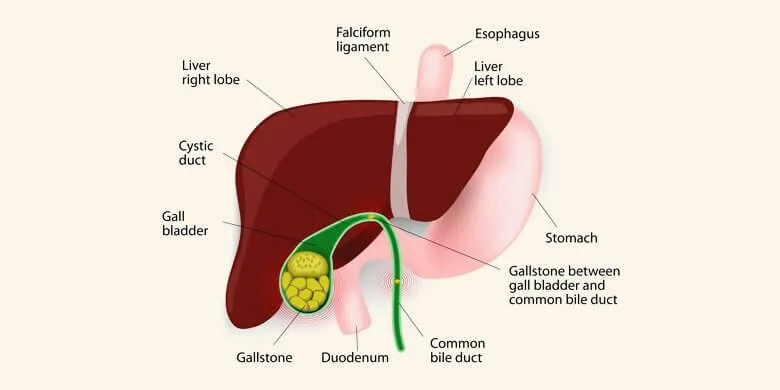
Before talking about the symptoms of gallbladder disease, you need to discuss its anatomy, location and function. Gall bladder is an organ which is a part of our biliary system. It acts as a storage area for the bile produced by the liver. Brief description of gallbladder is as follows.
- Anatomy: Gallbladder is a pear like hollow sac or a pouch-like structure.
- Location: it lies just below/under the liver.
- Function: The gallbladder function is to store bile which is a greenish-brown digestive juice. The liver secretes gall – an alternative term for bile. After that, it delivers this hepatic juice to the biliary vesicle for temporary storage. Finally, as the need arises, the digestive fluid reaches small intestine to aid in digestion.
For this reason, before a meal, the gall bladder is full of bile and appears to be the size of a small pear. However, after a meal, the bile goes to the intestines and, therefore, the organ looks completely flat.
Gallbladder Disease:
The term gallbladder disease is generally used for any condition that affects the gall bladder. However, depending upon the causative factor, the symptoms of gallbladder disease may vary. Majority of the diseases cause inflammation of gall bladder’s walls. Cholecystitis is the appropriate name for such a condition.
Usually, a gallbladder disease occurs when the ducts which lead to the intestine experience blockage by gall stones. Gallstones form when the substances in bile – including cholesterol, calcium and bile salts – form hard particles.
On one hand, these can be as large as a golf ball while, on the other, the stones may measure just the size of a sand particle. The condition often leads to gangrene. Apart from this, inflammation, scarring, infections and other diseases of the gall bladder are discussed further below along with the symptoms of gallbladder disease.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Disease:
The common symptoms of gallbladder disease are:
- Body Fever
- Intestinal Gas (Bloating, Flatulence, Belching)
- Pancreatitis
- Heart Problem or Heart Attack
- Indigestion
- Vomiting and Nausea
- Pain in the abdominal region
Here follows discussion about the symptoms of gallbladder disease in a bit detail.
Chronic Cholecystitis
 Chronic Cholecystitis is a condition that occurs after several attacks of acute Cholecystitis. In this condition, the gallbladder shrinks and is unable to perform its primary function of storing and releasing bile into the small intestine.
Chronic Cholecystitis is a condition that occurs after several attacks of acute Cholecystitis. In this condition, the gallbladder shrinks and is unable to perform its primary function of storing and releasing bile into the small intestine.
Symptoms:
The common symptoms of this disease include:
- Constant or recurring abdominal pain.
- Nauseous feeling which may often lead to vomiting.
Gallbladder Cancer:
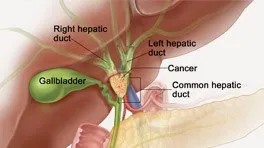 Although it is a very rare disease, if you do not treat it on time, it can cause the cancer to spread to other parts of the body.
Although it is a very rare disease, if you do not treat it on time, it can cause the cancer to spread to other parts of the body.
Symptoms:
The main symptoms include:
- Pain occurring in the abdomen after meals.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Constant fever or jaundice.
- Different colors of stool.
Choledocholithiasis:
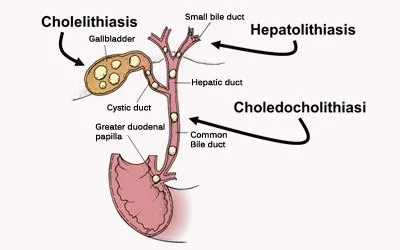 When gall stones enter the bile duct, they hinder the release of bile into the intestines. So this condition occurs as the result of blockage in the bile ducts. This causes inflammation or distention of the liver.
When gall stones enter the bile duct, they hinder the release of bile into the intestines. So this condition occurs as the result of blockage in the bile ducts. This causes inflammation or distention of the liver.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of gallbladder disease are as under:
- Extreme pain in the upper middle abdomen.
- Fever and chills.
- Nausea accompanied with consequent vomiting.
Sclerosing Cholangitis:
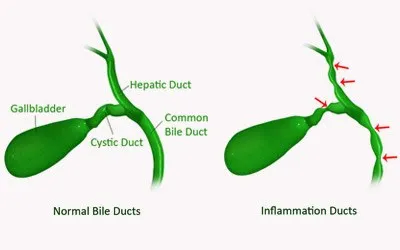 It occurs when there is scarring, damage or inflammation of the bile duct.
It occurs when there is scarring, damage or inflammation of the bile duct.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of this disease are below:
- The liver gets enlarged.
- A loss of appetite.
- Losing weight rapidly.
Acalculous Gallbladder Disease:
This condition occurs when the muscles and valves of the gallbladder are not working properly. Consequently, the following symptoms may appear.
Symptoms:
The symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain on the right side radiating up towards the shoulder.
- The patient may have loose stools or diarrhea.
- Vomiting and nauseous feeling.
- Swelling and bloating.
Gallbladder Polyps:
These are basically lesions or growth on the gall bladder. However, they are mostly harmless and very rare to occur.
Symptoms:
They often do not cause any symptoms at all. In some cases, the only symptom of gall bladder polyps is biliary colic. The particular symptom also radiates pain from the gallbladder.
Gangrene:
It occurs when the poor flow of blood hinders the proper functioning of the gall bladder.
Symptoms:
In this case, the main symptoms of gallbladder disease are:
- The person might develop a low blood pressure.
- Feeling pain in the gall bladder region.
- It also may lead to disorientation.
- Fever, nausea and gas will also be common in people suffering from gangrene.
Abscess of the Gallbladder:
The abscess occurs when an area of the body is inflamed with pus (accumulation of white blood cells, dead tissues and bacteria).
Symptoms:
The main symptom of this disease is that it presents itself in the form of pain. On the other hand, the pain occurs in the upper right side of the abdominal region. Therefore, if you are experiencing a constant pain in this region, it is best to go through checkup for abscess of the gall bladder.
The Main Concerns:
Individuals suffering from the above mentioned symptoms are likely to be the victim of some gallbladder disease. If they meet one or more of the following conditions, it should be a sign of serious concern for them. This is when they are most likely to be suffering from gall bladder diseases.
- Obesity
- Consuming a high-fat or a high-cholesterol diet
- Being a diabetic patient
- Aged 60 or above
- Taking medicines that contain estrogen
- Females have a higher risk of developing gall stones
- Having a history of gall stones in family
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Disease:
If a person shows the symptoms of gallbladder disease, they should immediately contact their doctor. The earlier the condition is detected, the better and easier it is to be treated. The doctor will run a few tests to confirm the symptoms and condition.
- The doctors may need the patient’s family history.
- Mostly a physical exam is also done to understand the condition.
- Ultrasonography is another popular method of detecting the disease.
- Other tests including blood tests, chest x-rays and abdomen x-rays also prove to be helpful.
Measures to Be Taken:
Those who are suffering from the symptoms of gallbladder disease or are at a risk due to family history should take the following measures and precautions. In this way, they can avoid the disease or, at least, make it less severe.
- Make a habit of eating a healthy and a well-balanced diet. At the same time, try to cut down on fat and cholesterol. Also consume fruits and vegetables in their original form. Avoid too much oily and fried food.
- Regular workout and exercise is a must thing to ensure proper functioning of your system.
- Drink plenty of water, which is an excellent way to keep your system clean, healthy and active.
- Get regular checkups from your doctor.
For treating the disease, if condition is mild, oral antibiotics are usually very helpful for the patient. However, if the episodes keep recurring and the condition goes worse, surgery becomes the only option. Mostly in the cases of gall stones a surgery has to be performed to get rid of the stones.


